Regulation Basics
NPRA was given the task of ensuring the quality, efficacy and safety of pharmaceuticals through the registration and licensing scheme. This is achieved through evaluation of scientific data and laboratory tests on all products before they are marketed. A system to monitor products in the market was set-up. Information on drugs to medical profession and consumer was made available through a drug information service.
1.0 Product Classification
It is important to determine the category of a product that falls within the food-drug interphase (FDI) whether the products are regulated as drug (health supplement or natural product under the NPRA’s purview) or, as food (under the FSQ’s purview) because different regulatory requirements apply. Therefore, the following flowchart serves only as guide to help you determine the category of the product that falls within the FDI
1.1
2.0 QUEST3+ System Basic
3.0 ASEAN Guidance Documents
ASEAN Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use
(The following were abstracted from the Health Sciences Authority Singapore site)
ASEAN Common Technical Dossier (ACTD)
- Organisation of the Dossier
- Glossary used for the ACTD and ACTR
- Part II: Quality
- Part III: Nonclinical Document
- Part IV: Clinical Document
- ACTD Clinical Check List for Product Classification
ASEAN Common Technical Requirements (ACTR)
- ASEAN Guideline on Submission of Manufacturing Process Validation Data for Drug Registration
- Annex A1 Guidance on Process Validation Scheme for Solid Oral Dosage Products
- Annex A2 Guidance on Process Validation Scheme for Aseptically Processed Products
- Annex A3 Guidance on Process Validation Scheme for Terminally Scheme for Terminally Sterilised Products
- Annex B Table of Content of Process Validation Documentation
- Annex D Glossary
- ASEAN Guidelines for Validation of Analytical Procedures
- 25PPWG ANNEX 7 (iv) Final ASEAN Guideline on Stability Study Drug Product R2
- ASEAN 1st Q & A to the ASEAN Stability Guideline R1 (21st ACCSQ PPWG)
- ASEAN Guidelines for the Conduct of Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies
- ASEAN Guideline on Process Validation Q&A
4.0 Guideline For The Submission Of Product Samples For Laboratory Testing
The submission of sample for laboratory testing is as part of the registration process. This guideline consists of the general and specific requirements for the submission of samples to the Centre for Quality Control for laboratory testing. The general requirements define the condition of the samples to be submitted whereas the specific requirements illustrate the additional details needed according to the category of product.
The applicant is given a period of 14 working days from the date of screening approval to send samples for laboratory testing. If the samples are not submitted within the specified time frame, the application will be rejected.
The applicants shall comply with these requirements and failure to meet any of these requirements may cause rejection of the samples.
5.0 Clinical Trials
Clinical trial is an expanding area of clinical research in Malaysia, and with the increasing complexity of clinical trials conducted in the country, it is essential to review current standards for compliance with international clinical trial standards and guidelines.
The primary purpose of the Malaysian Guideline for Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is to provide researchers, reviewers, sponsors and regulators of clinical trials a description of the fundamental principles and requirements that ensure regulatory compliance. The Malaysian GCP follows the same basic structure and format of the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) E6 Good Clinical practice Guideline.
Since the introduction of the first edition of the Malaysian GCP in 1999, more than 12,000 healthcare professionals and researchers have been GCP-trained and certified.
6.0 Reliance
Reliance in Regulatory Decision Making
The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines reliance as the act whereby the regulatory authority in one jurisdiction takes into account and gives significant weight to assessments performed by another regulatory authority or trusted institution, or to any other authoritative information, in reaching its own decision. The relying authority remains independent, responsible, and accountable for the decisions taken, even when it relies on the decisions, assessments, and information of others.
NPRA is committed to ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of medicinal products while facilitating timely public access through rigorous regulatory oversight. By practicing reliance, NPRA enhances regulatory efficiency, optimises resources, and accelerates access of essential medicines and vaccines to the public.
The reliance mechanism is applied by leveraging the work performed by other regulatory bodies on the same products intended for the local market. This mechanism is initiated to reduce duplication of effort and enables NPRA to emphasise the risk-based approach in regulatory activities. Reliance procedures provide a more efficient review process and ultimately early access to pharmaceutical products in the market.
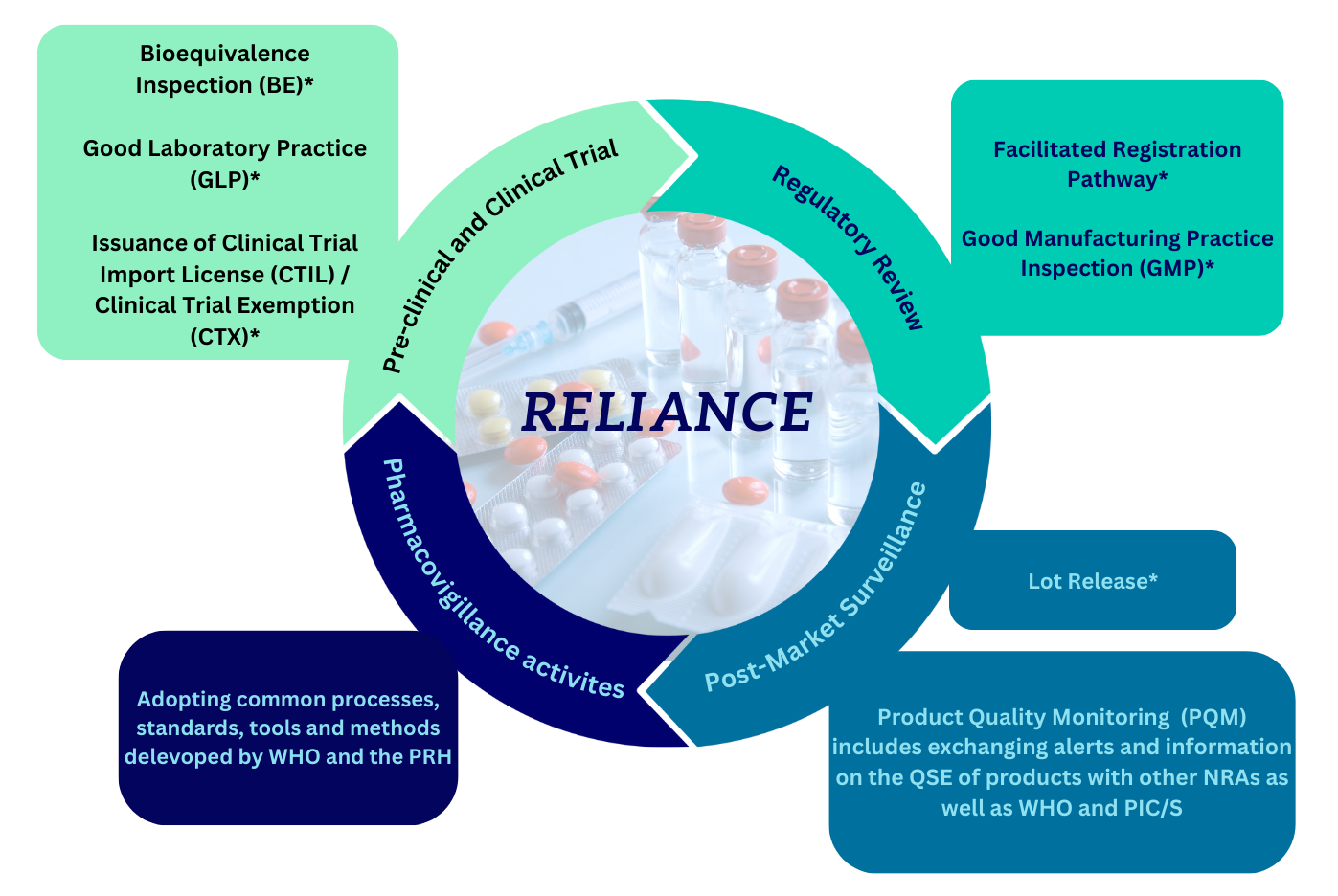
*Click on the link below to access the individual guidelines:
Approved National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs)
NPRA relies on the National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs) approved by the Drug Control Authority as listed below:
- European Medicines Agency (EMA)
- Health Canada
- Health Sciences Authority (HSA) Singapore
- Medicine and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency United Kingdom (UKMHRA)
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) Japan
- Swissmedic
- Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) Australia
- United States Food and Drug Authority (USFDA)
International Regulatory Cooperation
Malaysia adheres to the OECD Mutual Acceptance of Data (MAD) for Good Laboratory Practice (GLP). Therefore, NPRA accepts pivotal non-clinical safety study data (e.g., toxicology, reproductive toxicity, immunotoxicity) from OECD-MAD GLP-compliant laboratories in member and adherent countries without requiring duplicate testing. This also extends to recognizing GLP inspections and their outcomes from these countries.
NPRA is also a member of the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S). This enables NPRA to accept GMP certificates and inspection reports from other PIC/S member regulatory authorities (as listed on the PIC/S website) as well as National Regulatory Authorities with a cooperation agreement, such as an MRA, with PIC/S.
As an ASEAN member, NPRA also accepts GMP certificates and inspection reports from ASEAN Listed Inspection Services (ASEAN LIS) under the ASEAN Sectoral MRA for GMP Inspection. In addition, NPRA also accepts bioequivalence studies conducted at bioequivalence centres listed under the ASEAN MRA for Bioequivalence Study Reports of Generic Medicinal Products.